Welcome to our exploration of the Top Best Difficult Language in the World! Language is both a bridge and a barrier, and some tongues present more challenges than others. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of languages that test the limits of linguistic prowess and cultural understanding. From tonal complexities to intricate writing systems, we’ll uncover what makes these languages both fascinating and formidable. Whether you’re a language enthusiast seeking a new challenge or simply curious about the diverse tapestry of human communication, this blog is your gateway to unlocking the secrets of the world’s most difficult languages.
Mandarin

Mandarin Chinese, also known simply as Mandarin, is a tonal language with a rich history and cultural significance. With over a billion speakers worldwide, it holds a pivotal place in global communication. However, its complexity often intimidates learners, making it one of the most challenging languages to master.
The Uniqueness of Mandarin Characters – Best Difficult Language
One of the most striking features of Mandarin is its writing system, consisting of thousands of characters, each representing a word or concept. Unlike alphabetic languages, Mandarin characters require memorization and understanding of stroke order, making the written language a formidable barrier for learners.
Understanding stroke order is crucial in writing Mandarin characters. Each character follows a specific sequence of strokes, and deviating from this order can alter the meaning or render the character illegible. Moreover, the intricate composition of characters reflects the richness of Chinese culture and history.
Tones in Mandarin: A Challenge for Learners
Perhaps the most daunting aspect of Mandarin for beginners is its tonal nature. Mandarin utilizes four primary tones, each of which can change the meaning of a word. Mastering tone pronunciation requires careful listening and practice, as even a slight mispronunciation can lead to misunderstanding.
To overcome the challenge of tones, learners must engage in rigorous pronunciation practice. Utilizing resources such as audio recordings, language apps, and language exchange partners can help develop a keen ear for tone differentiation.
Complex Grammar Structures
In addition to tones and characters, Mandarin grammar presents its own set of challenges. The language lacks grammatical inflections, relying instead on word order and context to convey meaning. Sentence structures may differ significantly from those in English, requiring learners to adapt their thinking patterns.
Understanding the syntactical rules of Mandarin is essential for constructing coherent sentences. Mastery of sentence order, particle usage, and verb placement allows learners to express themselves effectively in spoken and written Mandarin.
Learning Resources for Mandarin
Despite its difficulty, numerous resources are available to aid learners in their Mandarin journey. From textbooks and online courses to immersive language programs, individuals have access to a wealth of materials designed to facilitate language acquisition.
Platforms such as Duolingo, Rosetta Stone, and HelloChinese offer interactive lessons and exercises tailored to Mandarin learners of all levels. These resources combine audio, visual, and kinesthetic learning techniques to enhance comprehension and retention.
Strategies for Mastering Mandarin
To succeed in mastering Mandarin, learners must employ effective learning strategies tailored to their individual needs and preferences. Consistent practice, cultural immersion, and perseverance are key components of language proficiency.
Regular practice is essential for language acquisition. Setting aside dedicated study time each day allows learners to reinforce vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation skills progressively.
Cultural Significance of Mandarin Proficiency
Beyond its linguistic challenges, Mandarin proficiency offers invaluable cultural insights and opportunities. Proficiency in Mandarin opens doors to business ventures, academic pursuits, and cross-cultural exchanges, fostering mutual understanding and collaboration on a global scale.
Overcoming Common Obstacles in Learning Mandarin
While learning Mandarin may seem daunting, overcoming common obstacles is achievable with determination and the right approach. By addressing challenges systematically and seeking support from fellow learners and educators, individuals can navigate the complexities of Mandarin more effectively.
Importance of Immersion and Practice
Immersing oneself in Mandarin-speaking environments accelerates language acquisition and cultural understanding. Whether through travel, language exchange programs, or virtual immersion experiences, exposure to authentic language usage enhances fluency and confidence.
Benefits of Learning Mandarin Despite Its Difficulty
Despite its challenges, learning Mandarin offers numerous personal and professional benefits. From enhanced cognitive abilities to expanded career opportunities, proficiency in Mandarin opens doors to new horizons and enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Read About: Top Best PC Games All Time In The World
Arabic – Best Difficult Language

Arabic, spoken by millions across the Middle East and North Africa, is renowned for its complexity and diversity. Its unique script, intricate grammar, and diverse dialects make it a formidable language for non-native speakers to learn.
The Complexity of Arabic Script
One of the most daunting aspects of Arabic for learners is its script. Written from right to left, Arabic script consists of intricate, connected characters that change shape depending on their position within a word. Mastery of Arabic calligraphy requires precision and patience.
Learning to write Arabic characters by hand is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor. Each letter has multiple forms depending on its position in a word, requiring learners to practice stroke order and letter connections diligently.
Unique Features of Arabic Grammar
Arabic grammar differs significantly from English and other Indo-European languages. It employs a system of root words and patterns to convey meaning, with intricate rules governing verb conjugation, noun declension, and sentence structure.
Understanding the root and pattern system is crucial for mastering Arabic grammar. Words are formed by combining root consonants with various patterns, resulting in a rich vocabulary with interconnected meanings.
Challenges Posed by Arabic Pronunciation
Arabic pronunciation presents challenges for non-native speakers, particularly due to the presence of sounds that do not exist in many other languages. Consonants and vowels are articulated differently, requiring learners to train their ears and mouths to produce unfamiliar sounds accurately.
To overcome pronunciation challenges, learners must engage in regular practice and exposure to Arabic speech. Utilizing audio resources, language partners, and immersive experiences can help develop a more authentic accent and intonation.
Resources for Learning Arabic
Despite its difficulty, numerous resources are available to aid learners in their Arabic journey. From textbooks and online courses to language exchange programs and cultural immersion experiences, individuals have access to a wealth of materials designed to facilitate language acquisition.
Platforms such as Mango Languages, ArabicPod101, and iTalki offer interactive lessons and resources for learners of all levels. These platforms provide a combination of audio, visual, and written materials to enhance comprehension and retention.
Strategies for Mastering Arabic
To succeed in mastering Arabic, learners must employ effective learning strategies tailored to their individual needs and preferences. Consistent practice, cultural immersion, and perseverance are key components of language proficiency.
Immersing oneself in Arabic-speaking environments accelerates language acquisition and cultural understanding. Language exchange programs, travel opportunities, and virtual immersion experiences provide invaluable exposure to authentic language usage.
Cultural Significance of Arabic Proficiency
Beyond its linguistic challenges, proficiency in Arabic offers invaluable cultural insights and opportunities. It fosters deeper connections with Arab communities, facilitates cross-cultural communication, and opens doors to diverse career paths and academic pursuits.
Overcoming Obstacles in Learning Arabic
While learning Arabic may seem daunting, overcoming common obstacles is achievable with determination and the right approach. By breaking down the language into manageable components, seeking support from educators and peers, and embracing mistakes as part of the learning process, learners can progress steadily toward fluency.
Importance of Immersion and Practice
Immersion and consistent practice are essential for language acquisition. Engaging with Arabic media, conversing with native speakers, and participating in cultural activities immerse learners in the language and reinforce their skills over time.
Benefits of Learning Arabic Despite Its Difficulty
Despite its challenges, learning Arabic offers numerous personal and professional benefits. From enhanced cultural awareness and global communication skills to expanded career opportunities and academic pursuits, proficiency in Arabic enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Read About: Top Best Rich Man All Time In The World
Japanese

Japanese, spoken by over 125 million people, is known for its complexity and diversity. Its three writing systems, including Kanji, Hiragana, and Katakana, along with intricate grammar and cultural nuances, make it a formidable language for learners.
Challenges Posed by Japanese Writing Systems – Best Difficult Language
The Japanese writing system comprises Kanji characters borrowed from Chinese, along with two phonetic scripts: Hiragana and Katakana. Mastering these writing systems requires memorization of thousands of characters and understanding their diverse readings and meanings.
Kanji, the logographic characters borrowed from Chinese, pose a significant challenge for learners. With over 2,000 commonly used characters, memorizing strokes, meanings, and pronunciations demands dedication and perseverance.
Complexities of Japanese Grammar
Japanese grammar differs significantly from English, featuring unique sentence structures, verb conjugations, and honorific language. Understanding and applying these grammatical nuances require careful study and practice.
Japanese verbs undergo various conjugations to express tense, mood, and politeness levels. Additionally, sentence structure in Japanese follows a subject-object-verb pattern, which may seem unfamiliar to English speakers.
Pronunciation Difficulties in Japanese
Japanese pronunciation presents challenges for non-native speakers, particularly due to the presence of sounds not found in English. Mastering pitch accent, vowel length, and subtle nuances of pronunciation is essential for clear communication.
Pitch accent plays a crucial role in Japanese pronunciation, with syllables pronounced at different pitch levels conveying distinct meanings. Learning to recognize and reproduce pitch patterns accurately is key to natural-sounding speech.
Resources for Learning Japanese
Despite its difficulty, numerous resources are available to aid learners in their Japanese journey. From textbooks and online courses to language exchange programs and immersive experiences, individuals have access to a wealth of materials designed to facilitate language acquisition.
Platforms such as WaniKani, Tae Kim’s Guide to Learning Japanese, and HelloTalk offer interactive lessons, flashcards, and language exchange opportunities for learners of all levels. These resources combine audio, visual, and kinesthetic learning techniques to enhance comprehension and retention.
Strategies for Mastering Japanese
To succeed in mastering Japanese, learners must employ effective learning strategies tailored to their individual needs and preferences. Consistent practice, cultural immersion, and perseverance are key components of language proficiency.
Immersing oneself in Japanese culture and language accelerates proficiency and cultural understanding. Language exchange programs, study abroad opportunities, and virtual immersion experiences provide invaluable exposure to authentic language usage.
Cultural Significance of Japanese Proficiency
Beyond its linguistic challenges, proficiency in Japanese offers invaluable cultural insights and opportunities. It fosters deeper connections with Japanese society, facilitates cross-cultural communication, and opens doors to diverse career paths and academic pursuits.
Overcoming Obstacles in Learning Japanese
While learning Japanese may seem daunting, overcoming common obstacles is achievable with dedication and the right approach. By breaking down the language into manageable components, seeking support from educators and peers, and embracing mistakes as part of the learning process, learners can progress steadily toward fluency.
Importance of Immersion and Practice
Immersion and consistent practice are essential for language acquisition. Engaging with Japanese media, conversing with native speakers, and participating in cultural activities immerse learners in the language and reinforce their skills over time.
Benefits of Learning Japanese Despite Its Difficulty
Despite its challenges, learning Japanese offers numerous personal and professional benefits. From enhanced cultural awareness and global communication skills to expanded career opportunities and academic pursuits, proficiency in Japanese enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Read About: Top Best Airports All Time In The World
Hungarian – Best Difficult Language

Hungarian, spoken by approximately 10 million people primarily in Hungary and parts of neighboring countries, is renowned for its complexity and linguistic uniqueness. Its distant relation to other European languages and rich historical roots contribute to its difficulty for learners.
Complexity of Hungarian Grammar
Hungarian grammar is notoriously complex, featuring numerous cases, suffixes, and agglutination. Understanding and applying these grammatical rules require meticulous study and practice.
Hungarian nouns and pronouns inflect for case, indicating their grammatical role in a sentence. With a total of 18 cases, including accusative, dative, and instrumental, learners must grasp the nuances of case usage for accurate communication.
Challenges Posed by Hungarian Pronunciation
Hungarian pronunciation presents difficulties for non-native speakers, particularly due to its vowel harmony system and unique consonant clusters. Mastering these phonetic intricacies is essential for clear and natural-sounding speech.
Hungarian employs a vowel harmony system, where vowels within a word must harmonize in terms of frontness or backness. Additionally, consonant clusters, such as “gy,” “ny,” and “zs,” pose challenges for learners unfamiliar with such combinations.
Unique Features of Hungarian Vocabulary
Hungarian vocabulary exhibits unique characteristics influenced by its linguistic history and cultural heritage. Loanwords from neighboring languages, as well as indigenous terms, contribute to the richness and complexity of Hungarian lexicon.
Hungarian vocabulary comprises loanwords borrowed from languages such as Turkish, German, and Slavic languages, alongside indigenous terms derived from Hungarian roots. Recognizing and understanding the origins of words enhances language comprehension and cultural appreciation.
Resources for Learning Hungarian
Despite its difficulty, various resources are available to aid learners in their Hungarian journey. From textbooks and online courses to language exchange programs and immersion experiences, individuals have access to diverse materials designed to facilitate language acquisition.
Structured language courses and private tutors offer personalized instruction tailored to learners’ proficiency levels and learning styles. These resources provide guided practice and feedback to enhance comprehension and fluency.
Strategies for Mastering Hungarian
To succeed in mastering Hungarian, learners must employ effective learning strategies tailored to their individual needs and preferences. Consistent practice, cultural immersion, and perseverance are essential components of language proficiency.
Immersing oneself in Hungarian culture and language accelerates proficiency and cultural understanding. Language exchange programs, study abroad opportunities, and virtual immersion experiences provide invaluable exposure to authentic language usage and cultural nuances.
Cultural Significance of Hungarian Proficiency
Beyond its linguistic challenges, proficiency in Hungarian offers invaluable cultural insights and opportunities. It fosters deeper connections with Hungarian society, facilitates cross-cultural communication, and opens doors to diverse career paths and academic pursuits.
Overcoming Obstacles in Learning Hungarian
While learning Hungarian may seem daunting, overcoming common obstacles is achievable with dedication and the right approach. By breaking down the language into manageable components, seeking support from educators and peers, and embracing mistakes as part of the learning process, learners can progress steadily toward fluency.
Importance of Immersion and Practice
Immersion and consistent practice are crucial for language acquisition. Engaging with Hungarian media, conversing with native speakers, and participating in cultural activities immerse learners in the language and reinforce their skills over time.
Benefits of Learning Hungarian Despite Its Difficulty
Despite its challenges, learning Hungarian offers numerous personal and professional benefits. From enhanced cognitive abilities and cultural awareness to expanded career opportunities and meaningful connections with Hungarian speakers, proficiency in Hungarian enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Read About: Top Best Largest Cities All Time In The World
Korean

Korean, spoken by over 75 million people primarily in North and South Korea, is known for its complexity and linguistic uniqueness. Its writing system, grammar, and cultural context make it a formidable language for learners.
Complexity of the Korean Writing System – Best Difficult Language
One of the most challenging aspects of Korean for learners is its writing system, known as Hangul. While phonetic in nature, Hangul consists of thousands of characters, each representing a sound or syllable. Mastery of Hangul requires memorization and understanding of character combinations.
Learning to read and write Hangul characters is essential for Korean proficiency. Each character has a distinct shape and pronunciation, and learners must practice stroke order and character combinations diligently.
Unique Features of Korean Grammar
It employs a system of honorifics, verb conjugations, and sentence structures that convey subtle nuances of politeness and respect.
Understanding honorifics is crucial for navigating Korean social interactions. Korean employs various levels of politeness in speech, with specific verb endings and speech patterns indicating the speaker’s relationship to the listener.
Challenges Posed by Korean Pronunciation
Korean pronunciation presents difficulties for non-native speakers, particularly due to its distinctive vowel and consonant sounds. Mastering correct pronunciation is essential for clear communication and comprehension.
Korean features a range of vowel and consonant sounds not found in English, such as aspirated consonants and double consonants. Pronouncing these sounds accurately requires attentive listening and practice.
Resources for Learning Korean
Despite its difficulty, numerous resources are available to aid learners in their Korean journey. From textbooks and online courses to language exchange programs and immersive experiences, individuals have access to diverse materials designed to facilitate language acquisition.
Platforms such as Talk to Me in Korean, KoreanClass101, and HelloTalk offer interactive lessons, podcasts, and language exchange opportunities for learners of all levels. These resources provide structured learning experiences and opportunities for real-world practice.
Strategies for Mastering Korean
To succeed in mastering Korean, learners must employ effective learning strategies tailored to their individual needs and preferences. Consistent practice, cultural immersion, and perseverance are key components of language proficiency.
Immersing oneself in Korean culture and language accelerates proficiency and cultural understanding. Language exchange programs, study abroad opportunities, and virtual immersion experiences provide invaluable exposure to authentic language usage and cultural nuances.
Cultural Significance of Korean Proficiency
Beyond its linguistic challenges, proficiency in Korean offers invaluable cultural insights and opportunities. It fosters deeper connections with Korean society, facilitates cross-cultural communication, and opens doors to diverse career paths and academic pursuits.
Overcoming Obstacles in Learning Korean
While learning Korean may seem daunting, overcoming common obstacles is achievable with dedication and the right approach. By breaking down the language into manageable components, seeking support from educators and peers, and embracing mistakes as part of the learning process, learners can progress steadily toward fluency.
Importance of Immersion and Practice
Immersion and consistent practice are essential for language acquisition. Engaging with Korean media, conversing with native speakers, and participating in cultural activities immerse learners in the language and reinforce their skills over time.
Benefits of Learning Korean Despite Its Difficulty
Despite its challenges, learning Korean offers numerous personal and professional benefits. From enhanced cognitive abilities and cultural awareness to expanded career opportunities and meaningful connections with Korean speakers, proficiency in Korean enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Read About: Top Best Big Cities All Time In The World
Finnish – Best Difficult Language
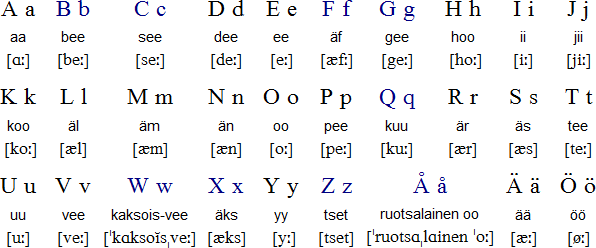
Finnish, spoken by approximately 5 million people primarily in Finland, is renowned for its complexity and linguistic uniqueness. Its distinct grammar, vowel harmony, and agglutinative nature make it a formidable language for learners.
Complexity of Finnish Grammar
One of the most daunting aspects of Finnish for learners is its grammar, which features a rich system of cases, verb conjugations, and word endings. Understanding and applying these grammatical rules require careful study and practice.
Finnish nouns and pronouns inflect for a wide range of cases, indicating their grammatical roles in sentences. With a total of 15 cases, including nominative, genitive, and accusative, learners must grasp the nuances of case usage for accurate communication.
Challenges Posed by Finnish Pronunciation
Finnish pronunciation presents difficulties for non-native speakers, particularly due to its distinctive vowel sounds and complex consonant clusters. Mastering correct pronunciation is essential for clear communication and comprehension.
Finnish employs a system of vowel harmony, where vowels within a word must harmonize in terms of frontness or backness. Additionally, Finnish features complex consonant clusters, such as “rk,” “nt,” and “lt,” which can be challenging to pronounce for learners.
Unique Features of Finnish Vocabulary
Finnish vocabulary exhibits unique characteristics influenced by its linguistic history and cultural heritage. Loanwords from neighboring languages, as well as indigenous terms, contribute to the richness and complexity of Finnish lexicon.
Finnish vocabulary comprises loanwords borrowed from languages such as Swedish, Russian, and German, alongside indigenous terms derived from Finnish roots. Recognizing and understanding the origins of words enhances language comprehension and cultural appreciation.
Resources for Learning Finnish
Despite its difficulty, various resources are available to aid learners in their Finnish journey. From textbooks and online courses to language exchange programs and immersive experiences, individuals have access to diverse materials designed to facilitate language acquisition.
Structured language courses and immersive programs offer comprehensive instruction in Finnish language and culture. These resources provide guided practice, cultural immersion, and opportunities for real-world communication with native speakers.
Strategies for Mastering Finnish
To succeed in mastering Finnish, learners must employ effective learning strategies tailored to their individual needs and preferences. Consistent practice, cultural immersion, and perseverance are essential components of language proficiency.
Immersing oneself in Finnish culture and language accelerates proficiency and cultural understanding. Language exchange programs, study abroad opportunities, and virtual immersion experiences provide invaluable exposure to authentic language usage and cultural nuances.
Cultural Significance of Finnish Proficiency
Beyond its linguistic challenges, proficiency in Finnish offers invaluable cultural insights and opportunities. It fosters deeper connections with Finnish society, facilitates cross-cultural communication, and opens doors to diverse career paths and academic pursuits.
Overcoming Obstacles in Learning Finnish
While learning Finnish may seem daunting, overcoming common obstacles is achievable with dedication and the right approach. By breaking down the language into manageable components, seeking support from educators and peers, and embracing mistakes as part of the learning process, learners can progress steadily toward fluency.
Importance of Immersion and Practice
Engaging with Finnish media, conversing with native speakers, and participating in cultural activities immerse learners in the language and reinforce their skills over time.
Benefits of Learning Finnish Despite Its Difficulty
Despite its challenges, learning Finnish offers numerous personal and professional benefits. From enhanced cognitive abilities and cultural awareness to expanded career opportunities and meaningful connections with Finnish speakers, proficiency in Finnish enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Read About: Top Best Tech Companies All Time In The World
Basque
Basque, spoken primarily in the Basque Country spanning parts of Spain and France, is a language isolate, meaning it has no known relatives. Its distinctiveness and lack of related languages make it a particularly challenging language for learners.
One of the most notable challenges of learning Basque is its complex grammar structure. Basque features ergative-absolutive alignment, extensive use of agglutination, and a rich system of noun declensions, verb conjugations, and case markings.
Basque grammar employs an ergative-absolutive alignment, where the subject of an intransitive verb is marked differently from the subject of a transitive verb. This feature is rare among world languages and requires learners to grasp a different conceptual framework.
Challenges Posed by Basque Pronunciation – Best Difficult Language
Basque pronunciation presents difficulties for non-native speakers due to its unique phonetic inventory and subtle phonological distinctions. Mastering correct pronunciation is essential for clear communication and comprehension.
Basque features phonemes not found in other Indo-European languages, such as the voiceless lateral fricative [ɬ] and the apical trill [r̄]. Additionally, it distinguishes between various vowel lengths and nasalization, requiring learners to develop keen auditory discrimination skills.
Unique Features of Basque Vocabulary
Basque vocabulary exhibits unique characteristics influenced by its linguistic history and cultural heritage. Loanwords from neighboring languages, as well as indigenous terms, contribute to the richness and complexity of Basque lexicon.
Basque vocabulary includes loanwords borrowed from languages such as Latin, Spanish, and French, alongside indigenous terms derived from Basque roots. Understanding the etymology and usage of words enhances language comprehension and cultural appreciation.
Resources for Learning Basque
Despite its difficulty, various resources are available to aid learners in their Basque journey. From textbooks and online courses to language exchange programs and immersion experiences, individuals have access to diverse materials designed to facilitate language acquisition.
Structured language courses and immersive programs offer comprehensive instruction in Basque language and culture. These resources provide guided practice, cultural immersion, and opportunities for real-world communication with native speakers.
Strategies for Mastering Basque
To succeed in mastering Basque, learners must employ effective learning strategies tailored to their individual needs and preferences. Consistent practice, cultural immersion, and perseverance are essential components of language proficiency.
Immersing oneself in Basque culture and language accelerates proficiency and cultural understanding. Language exchange programs, study abroad opportunities, and virtual immersion experiences provide invaluable exposure to authentic language usage and cultural nuances.
Cultural Significance of Basque Proficiency
Beyond its linguistic challenges, proficiency in Basque offers invaluable cultural insights and opportunities. It fosters deeper connections with Basque society, facilitates cross-cultural communication, and promotes preservation of Basque heritage and identity.
Overcoming Obstacles in Learning Basque
While learning Basque may seem daunting, overcoming common obstacles is achievable with dedication and the right approach. By breaking down the language into manageable components, seeking support from educators and peers, and embracing mistakes as part of the learning process, learners can progress steadily toward fluency.
Importance of Immersion and Practice
Immersion and consistent practice are crucial for language acquisition. Engaging with Basque media, conversing with native speakers, and participating in cultural activities immerse learners in the language and reinforce their skills over time.
Benefits of Learning Basque Despite Its Difficulty
Despite its challenges, learning Basque offers numerous personal and professional benefits. From enhanced cognitive abilities and cultural awareness to expanded career opportunities and meaningful connections with Basque speakers, proficiency in Basque enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Read About: Top Best Programming Languages All Time In The World
Navajo – Best Difficult Language
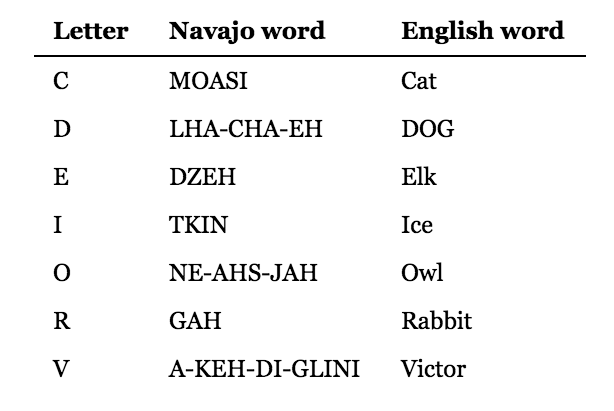
The Navajo language belongs to the Na-Dené family of languages, which is primarily spoken by the Navajo people residing in the states of Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. With roots deeply embedded in Navajo culture and tradition, the language serves as a crucial aspect of their identity and heritage.
Unique Features of Navajo Language
One of the defining characteristics of the Navajo language is its complex grammar structure. Navajo employs an agglutinative grammar system, where words are formed by adding prefixes, suffixes, and infixes to root words, resulting in lengthy and intricate constructions.
Navajo is also a tonal language, wherein the pitch or tone of a word can change its meaning entirely. This tonality adds another layer of complexity for learners, as mastering the correct intonation is essential for accurate communication.
Historical Context of Navajo Language
The history of the Navajo language is deeply intertwined with the cultural heritage of the Navajo people. Traditionally, the language was transmitted orally from generation to generation, serving as a means of preserving tribal knowledge, stories, and traditions.
Challenges Faced by Learners of Navajo Language
Despite its rich cultural significance, learning the Navajo language can be exceptionally challenging for non-native speakers due to several factors:
Verb Conjugation Complexity
Navajo verbs exhibit intricate conjugation patterns, which can vary based on factors such as tense, aspect, mood, and subject agreement. Navigating through these conjugations requires a deep understanding of the language’s grammatical intricacies.
Verb Theme Variation
In Navajo, verbs are categorized into different thematic groups, each with its own set of conjugation rules and suffixes. Learners must memorize these thematic variations, adding another layer of complexity to language acquisition.
Pronoun Incorporation
Navajo employs a unique grammatical feature known as pronoun incorporation, where subject and object pronouns are incorporated directly into verbs. This feature adds complexity to sentence structure and requires learners to master the intricacies of pronoun placement.
Preservation Efforts and Initiatives
Recognizing the importance of preserving the Navajo language, various initiatives and organizations have been established to promote its usage and revitalization. These efforts include language immersion programs, educational resources, and community-driven initiatives aimed at fostering intergenerational transmission.
Importance of Navajo Language in Modern Context
In contemporary society, the Navajo language continues to play a vital role in preserving cultural heritage, fostering community cohesion, and promoting indigenous identity. Additionally, the language serves as a bridge to traditional knowledge systems, environmental stewardship, and holistic well-being.
Read About: Top Best Movies All Time In The World
Icelandic

Icelandic, the official language of Iceland, traces its origins back to Old Norse, the language of the Vikings. Over centuries, Icelandic has evolved into a distinct language, characterized by its archaic grammar, rich vocabulary, and literary heritage.
Unique Features of Icelandic Language – Best Difficult Language
One of the defining features of Icelandic is its complex grammar and syntax. Icelandic employs a highly inflected grammar system, where words undergo extensive changes to convey meaning. This includes noun declensions, verb conjugations, and intricate word order rules, making it challenging for learners to grasp.
Icelandic retains many elements of its Old Norse roots, including archaic vocabulary, poetic forms, and grammatical structures. This historical influence adds depth and complexity to the language, as learners must familiarize themselves with medieval texts and literary traditions.
Historical Context of Icelandic Language
The Icelandic language has a rich historical context, closely intertwined with the cultural heritage of Iceland. Throughout history, Icelandic has served as a medium for preserving Norse sagas, epic poetry, and medieval manuscripts, contributing to its status as a literary treasure.
Challenges Faced by Learners of Icelandic Language
Despite its cultural significance, learning Icelandic poses several challenges for non-native speakers:
Icelandic grammar is notoriously complex, requiring learners to master intricate rules governing noun declensions, verb conjugations, and syntactic structures. Additionally, the language features numerous irregularities and exceptions, further complicating the learning process.
Pronunciation Challenges
Icelandic pronunciation can be difficult for non-native speakers, as it features unique sounds and phonetic distinctions not found in other languages. Mastering the correct pronunciation of vowels, consonants, and diphthongs requires dedicated practice and exposure to native speakers.
Vocabulary and Idioms
Icelandic boasts a rich vocabulary, including archaic words, poetic expressions, and idiomatic phrases derived from Old Norse literature. For learners, navigating this extensive lexicon presents a significant challenge, as many words have nuanced meanings and cultural connotations.
Preservation Efforts and Initiatives
Recognizing the importance of preserving the Icelandic language, various initiatives and organizations have been established to promote its usage and revitalization. These efforts include language immersion programs, educational resources, and cultural initiatives aimed at fostering linguistic heritage.
Importance of Icelandic Language in Modern Context
In contemporary society, Icelandic continues to play a vital role in shaping national identity, cultural expression, and literary heritage in Iceland. Additionally, the language serves as a bridge to the country’s rich literary tradition, connecting modern readers with medieval texts and sagas.
Read About: Top Best Mobiles All Time In The World
Polish – Best Difficult Language

Polish, the official language of Poland, belongs to the West Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family. With over 40 million speakers worldwide, Polish serves as a vital means of communication and cultural expression for the Polish people.
Unique Features of Polish Language
One of the defining features of the Polish language is its complex grammar and conjugation system. Polish employs a rich array of grammatical cases, verb forms, and syntactic structures, requiring learners to navigate through intricate rules and exceptions.
Polish is highly inflected, with nouns, adjectives, and pronouns undergoing extensive inflection to indicate grammatical case, number, and gender. This inflectional system adds layers of complexity to sentence structure and word usage, challenging learners to master the nuances of declension and agreement.
Historical Context of Polish Language
The history of the Polish language is deeply intertwined with the cultural and political evolution of Poland. Throughout centuries of tumultuous history, Polish has served as a symbol of national identity, resistance, and resilience against external influences.
Challenges Faced by Learners of Polish Language
Despite its cultural significance, learning Polish presents several challenges for non-native speakers:
Polish pronunciation can be difficult for learners due to the presence of unique consonant clusters, vowel sounds, and nasal vowels. Mastering correct pronunciation requires attentive practice and exposure to native speakers.
Polish verbs exhibit a complex system of aspect and tense, with distinctions between perfective and imperfective aspects. Understanding when to use each aspect and conjugating verbs accordingly can be challenging for learners.
Polish nouns are gendered, with masculine, feminine, and neuter genders, each requiring different forms of adjectives, pronouns, and verb agreement. Navigating gender agreement rules adds complexity to sentence construction and comprehension.
Preservation Efforts and Initiatives
Recognizing the importance of preserving the Polish language, various initiatives and organizations have been established to promote its usage and revitalization. These efforts include language education programs, cultural events, and the publication of Polish literature and media.
Importance of Polish Language in Modern Context
In contemporary society, Polish continues to play a vital role in shaping national identity, cultural expression, and intellectual discourse in Poland and beyond. Additionally, the language serves as a gateway to Poland’s rich literary tradition, scientific achievements, and artistic endeavors.
Read About: Top Best Market All Time In The World





